
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

Language added to a New York State budget bill is threatening to undermine a municipal broadband grant program established by Gov. Kathy Hochul’s office earlier this year.
Known as the Municipal Infrastructure Program, it was designed to provide grant funding for municipalities in the state eager to build publicly-owned, locally controlled broadband infrastructure as a way to ensure ubiquitous, affordable access to high-quality Internet after decades of frustration with expensive, spotty and uneven service from the regional monopolies.
Currently, New York state lawmakers are in the midst of budget proposal season in which the Governor’s office and both legislative chambers (the state Senate and Assembly) have until April 1 to reconcile and complete a final budget for the upcoming fiscal year.
Buried near the bottom of the Assembly budget proposal (A8805B) is a Trojan horse legislative sources say is being pushed by lobbyists representing Charter Spectrum, the regional cable monopoly and 2nd largest cable company in the U.S. that was nearly kicked out of New York by state officials in 2018 for atrocious service.
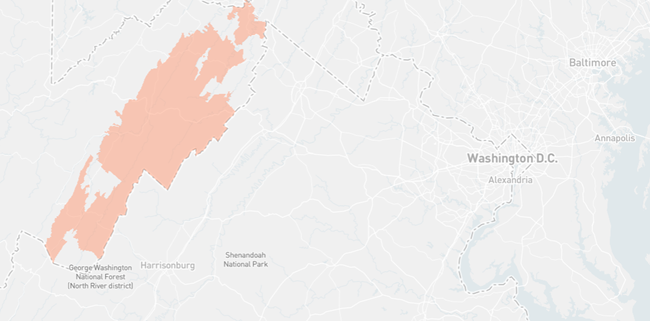
The rocky rural hills of West Virginia are a formidable foe when it comes to building high-speed Internet infrastructure that offers affordable high-quality service.
Nobody knows that better than Hardy Telecommunications (OneNet), a small community-owned cooperative that delivers affordable fiber to frustrated locals deemed too costly and cumbersome to be served by the incumbent telecom giants.
The cooperative serves parts of four counties (Hardy, Pendelton, Grant, and Hampshire). It connected its first fiber customer in 2013, after receiving $31.6 million in federal BTOP funding. Since then, the cooperative tells ILSR they’ve spent $20 million of their own funds to bring fiber to rural corners of the aptly-named Mountain State.
Derek Barr, Assistant General Manager at Hardy Telecommunications, says the cooperative currently delivers broadband service to 5,050 rural subscribers – 4,736 of which are on fiber lines that simply wouldn’t exist without federal funding programs. Hardy Telecommunications also provides 68 customers with fixed wireless access (FWA) broadband service.
“Our focus is fiber, and we're trying to build out fiber as much as we can,” Barr tells ILSR. “But it's very tough in our serving region. It's all mountains and a lot of trees, and a big chunk of our area is either state park or national forest land. It's also very hard to do fixed wireless because even if it might work in the winter, it's not going to work in the summer” when tree leaves block line of sight, he noted.
So the cooperative slowly and consistently expands fiber as it can, often in partnership with Pendleton County. As a result, locals have the option of a variety of double and triple play phone, cable, and fiber options, starting with a symmetrical 100 Mbps (megabit per second) downstream, 50 Mbps upstream fiber and phone bundle for $79 a month.
One year after launching a municipal fiber network, Dryden, NY officials say they’re making steady progress in their quest to expand affordable fiber broadband to the entire town of 14,500.
While the effort hasn’t been without obstacles, town leaders say the public response to their foray into broadband has been overwhelmingly positive.
“While there are challenges, we are continuing to make great progress in the buildout,” Dryden Town Supervisor Jason Leifer tells ILSR. “We have support from our residents, who continue to show interest in this project. We also have financial support from Tompkins County in the form of grants–and from neighboring municipalities who are interested in replicating our model.”
The city’s network began with a 50-home trial pilot trial in the southwest part of town. The broader $15 million network will be funded by a combination of bonds, $2 million in federal COVID-19 disaster relief funding, an Appalachian Regional Commission grant, and eventually, subscriber revenues.
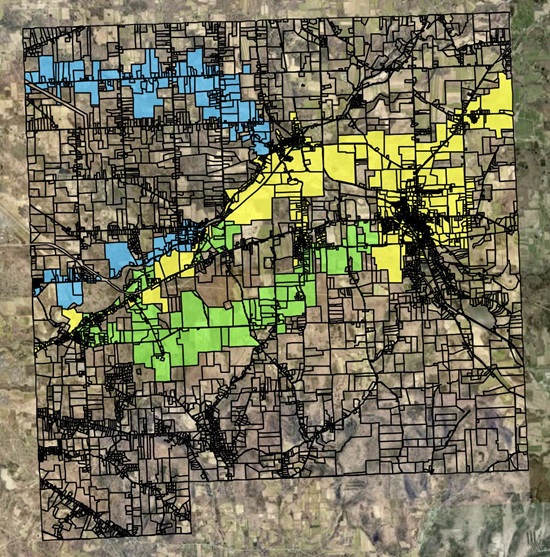
The town took a phased approach to deployment, first by connecting the backbone of the network in the southeast of the city, followed by a focus on the western and eastern halves of the municipality, respectively. The Dryden fiber website features a build map that helps locals track network progress.
“We have currently passed over 420 addresses with our buildout,” freshly-appointed Dryden Fiber Executive Director David Makar tells ISLR. “This includes over 150 rental properties – mostly single family homes and apartments – as well as many owner occupied homes and businesses. We are still in phase one, and as we move into the village of Dryden and the hamlets of Varna, Ellis Hollow, and Etna, we will be in phase two.”
The Tribal Broadband Bootcamps (TBB) – a three-day intensive learning experience focused on building and running Tribal Internet networks – are becoming even more immersive as the 12th TBB is now underway at the homestead of TBB co-founder Matthew Rantanen.
As more Tribal nations build out their own broadband networks to deliver service to Indigenous communities in the most disconnected areas of North America, broadband-minded Tribal leaders and instructors continue to gather in different Tribal regions across the country several times a year for the ultimate Indian Country networking experience.
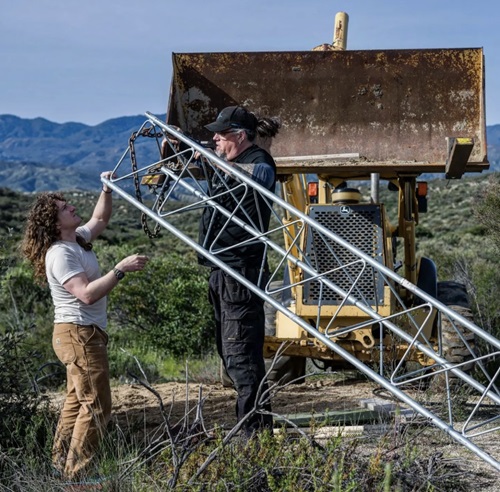

This time participants descended on “RantanenTown Ranch” in Aguanga, California – part of southern California’s Inland Empire region near Temecula.
With help from ILSR’s Community Broadband Networks Initiative Director and TBB co-founder Christopher Mitchell, and a handful of other instructors, the ranch has been transformed into a working demonstration site so participants could better learn the technologies involved in constructing broadband networks, while taking a deep-dive into what it takes to operate a network.
All of the previous bootcamps offered hands-on training. But, this particular bootcamp took it up a notch as TBB instructors set up a full deployment demonstration, illustrating how fiber is buried and/or deployed aerially.
Digging In
For decades, ILSR has recognized that communities need to be engaged on Internet access issues to make sure that everyone – from low-income, historically marginalized residents to small businesses and even municipal departments – have the Internet access they need to thrive in the digital age.
Digital equity is essential to help resolve other challenges and the current chasm between the haves and have-nots makes solving many other challenges – like education – more difficult.
To further the quest for greater digital inclusivity, recently ILSR’s Community Broadband Networks Initiative Director Christopher Mitchell put together a panel for Net Inclusion 2024, a conference convened by the National Digital Inclusion Alliance (NDIA) that drew 1300 attendees and was by far the largest digital inclusion conference held in many years of doing this work.
Entitled “Without Political Power, There is No Path to Digital Equity,” the panel was originally going to focus on the importance of structural change – and how we cannot ensure everyone is connected by relying solely on the networks already present in neighborhoods that see quite low broadband penetration. Instead, the panel discussion went a bit deeper than that and landed on an observation often made by Joshua Edmonds from Digital C in Cleveland. To paraphrase Joshua, we cannot coupon our way to digital equity.
Peppered by winding country roads and remote islands, Maine exemplifies the challenges in even deployment of affordable broadband. But thanks to tenacious island communities and forward-thinking state leadership, a growing roster of community-owned broadband networks are leading the charge toward affordable access in the Pine Tree State.
Peggy Schaffer, former executive director of the state of Maine's broadband mapping and expansion effort, ConnectMaine, has played a starring role in shoring up Maine’s broadband mapping data after years of federal dysfunction.
Schaffer’s well versed in the broad array of challenges faced by remote Maine communities, and says she’s long been impressed by the “scrappy” nature of Maine’s community-owned island deployments, which have faced down and overcome no limit of onerous challenges in an ongoing quest to finally bridge the state’s long standing digital divide.
Maine is currently ranked 49th in the U.S. in terms of resident access to gigabit-capable broadband service. Like so much of the country, the state is heavily dominated by regional monopolies that failed to uniformly deliver affordable, next-generation broadband, despite decades of federal subsidies, regulatory favors, and tax breaks.
Now local Maine communities are taking matters into their own hands, beginning with long-neglected island residents no stranger to unique logistical challenges.

‘It’s A Story Of Perseverance’
Martinsville, Virginia has technically owned a municipal fiber network for the better part of a generation. But the city never had the time, resources, or interest in maximizing the Municipal Internet Network’s (MINet) full potential until COVID demonstrated the importance of affordable access and federal broadband grants made expansion a viable reality.
At a Martinsville city council meeting on February 13, the council offered unanimous support for a phased expansion of the city’s fiber network.
What exactly the expansion will look like, and how it will be funded, very much remain a work in progress.
The core MINet fiber network originally consisted of 48 strands and 20 miles of fiber connecting city schools, municipal buildings, local businesses, and key anchor institutions. A 2009 estimate indicates the network has saved the city between $100,000 and $150,000 annually on telecom lease agreements every year since its inception.
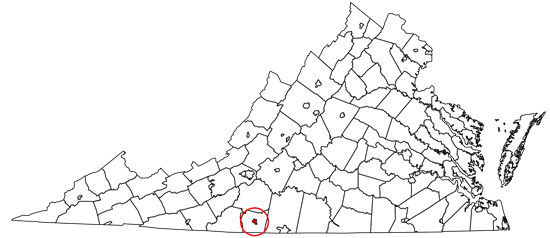
Despite having been first constructed in the 1990s, Martinsville’s MINet only has about 376 customers (98 of them being residential) in a city of nearly 14,000 residents. There’s roughly 20 users currently on a multi-month waiting list, eager to get access to affordable fiber at speeds up to a gigabit per second (Gbps).
Mike Scaffidi has been the MINet director for 26 years. He tells ILSR that while the city has contemplated network expansion for a long time, the city never had the staff or resources to prioritize the expansion or marketing of the city-owned fiber network.
In January, we released our new census of municipal networks in the United States for 2024, and the significant growth that we've seen over the last two years as more and more cities commit to building Internet infrastructure to add new tools for their local government, incentivize new economic development, and improve connectivity for households.
The trend has not gone unnoticed by the monopoly players and their allies; we've seen new dark-money campaigns on both the East Coast and in the west, as astroturf campaigns and misinformation efforts have increased.
A new short documentary by Light Reading does a great job of outlining the stakes for local governments, residents stuck on poor connections, and the incumbents as the wave of municipal networks grows. Featuring the network in Loveland, Colorado and context by advocates like the American Association for Public Broadband (AAPB) Executive Director Gigi Sohn and Washington State Representative Drew Hansen, it's well worth watching.
Colorado has long been home to some of the most innovative municipal broadband projects in the country. That trend has only accelerated with last year’s voter-approved elimination of municipal broadband restrictions, and it’s now being buoyed by a massive new wave of state grants that should further expand affordable broadband to long-neglected parts of the state.
Colorado Gov. Jared Polis recently announced the first of multiple broadband investments using stimulus funding from the U.S. Treasury’s Capital Projects Fund (CPF) program. The CPF is funded by $10 billion made possible by the American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA), and is a key part of the state’s goal to bring affordable broadband to 99 percent of Colorado residents by 2027.
According to the Governor’s office, the state just authorized $113 million in CPF funds on 13 projects that will bring fiber service to nearly 19,000 homes and businesses across Colorado. State officials say the funding will be heavily focused on projects in the South and Southwest portion of the Centennial State, where connectivity needs are greatest.

The Colorado Broadband Office says it received 112 applications asking for more than $642 million in broadband funding across the state–five times greater than the allotted awards.
Municipal finance is not for the weary.
But for the wise – at least according to the number-crunchers enmeshed in that world – one particular sliver of municipal finance (issuing bonds) has long been a viable way for local communities to finance the construction of municipal broadband networks. And as one Communication Union District in Vermont has discovered, bonding is better – when it’s rated.
Shining a light on bond-backed municipal broadband projects is the recent announcement that ECFiber, Vermont's first Communications Union District (CUD), obtained a BB rating from Standard & Poor Global, the nation’s preeminent credit rating agency. The rating will allow ECFiber to pay lower borrowing costs to complete a network expansion project.

“This is a historic moment,” Stan Williams, ECFiber’s municipal finance advisor said in a prepared statement. “For the first time, a CUD will be issuing a rated bond, which means that many more investors will be competing to buy those bonds, lowering the interest rate. ECFiber has been managed for its entire existence to reach this goal. It’s hard to overstate the importance of this achievement.”
East Central Vermont Telecommunications District governing board chairman F. X. Flinn added that the new bond rating "was made possible by over 16 years of grass-roots persistence, driven by a conviction that working together, our region could overcome the failure of the marketplace to offer decent broadband to all our homes and businesses."